(Click the below link for a Microsoft Word version of this blog-post)
(Click the below link for a pdf version of this blog-post)
What is an Integer?
In Mathematics:
An integer is a number that has no fractional[1] component. The term ‘integer’ in Latin means ‘whole.’ So an Integer is a Whole Number[2]. A person who practises wholesome behaviour is a person with integrity.
In Number Theory, the set of integers is very often represented by a boldface Capital ‘Z’[3]:
Z
Sometimes, in Number Theory, the set of integers is represented by a blackboard bold ‘Z’:
The set of integers comprises:
- the number:
0
- the sequence of positive Natural Numbers:
{1, 2, 3, 4, 5…}
- the sequence of negative integers:
{-1, -2, -3, -4, -5…}
In Python:
In Python, integers are a datatype. This datatype is assigned the keyword:
int
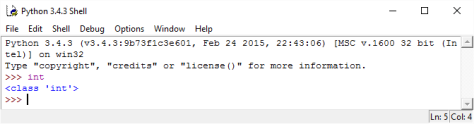
Figure 1: In Python, the int keyword represents the integer datatype.
In Python, we can use the:
int()
method so as to convert numbers that might exist as strings, or other datatypes, to integers:
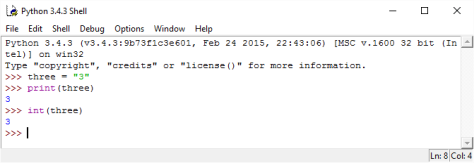
Figure 2: In the above example, we convert the number, 3, from a Python string to a Python integer by using the int() method. This is called ‘type conversion.’
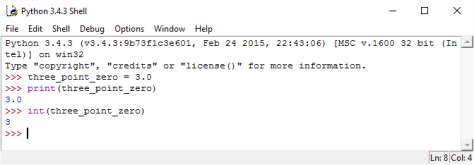
Figure 3: In the above example, we convert the number, 3.0, from a Python float to a Python integer by using the int() method. This is called ‘type conversion.’
Glossary:
integer
- noun.
- a number which is not a fraction; a whole number.
- a thing complete in itself.
<ORIGIN early 16th century (as an adjective meaning ‘entire, whole’): from Latin, ‘intact, whole’, from in– (expressing negation) + the root of tangere ‘to touch’. Compare with ENTIRE, also with Integral, integrate, and INTEGRITY[4].
<ETYMOLOGY> From the Latin 1st-and-2nd-declension adjective, ‘integra, integer, integrum,’ which means ‘complete,’ ‘whole,’ ‘intact.’ From the Latin prefix ‘in-,’ which expresses negation; and the Latin verb ‘tangō, tangere, tetigī, tāctum,’ which means ‘to touch.’ Etymologically, therefore, an ‘integer’ is a number that is ‘intact’ i.e. which does not have a fractional component.
[1] Whereas ‘integer’ comes from the Latin word for ‘whole,’ ‘fraction’ comes from the Latin supine ‘frāctum,’ which means ‘broken.’ The term ‘fraction’ is derived from the Latin 3rd-conjugation verb, frangō, frangere, frēgī, frāctum,’ which means ‘to break,’ ‘to shatter.’ If something be fragile, then it is easily broken; it is liable to shatter. A fraction, etymologically, is like a broken-off piece of a number.
[2] I speak, here, in general parlance. Mathematically, some would argue a difference between whole numbers and integers. Mathematicians sometimes regard whole numbers as comprising the sequence of positive integers: {0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5…}. I am merely trying to get across the concept that an Integer has no fractional part.
[3] The ‘Z’ represents the plural of the German feminine noun, ‘die Zahl,’ ‘the number,’ which is ‘die Zahlen.’
[4] Oxford University Press. Oxford Dictionary of English (Electronic Edition). Oxford. 2010. Loc 357261

